Autonomous Vehicles are Key Factors in Intelligent Transport Systems & Industrial Automation
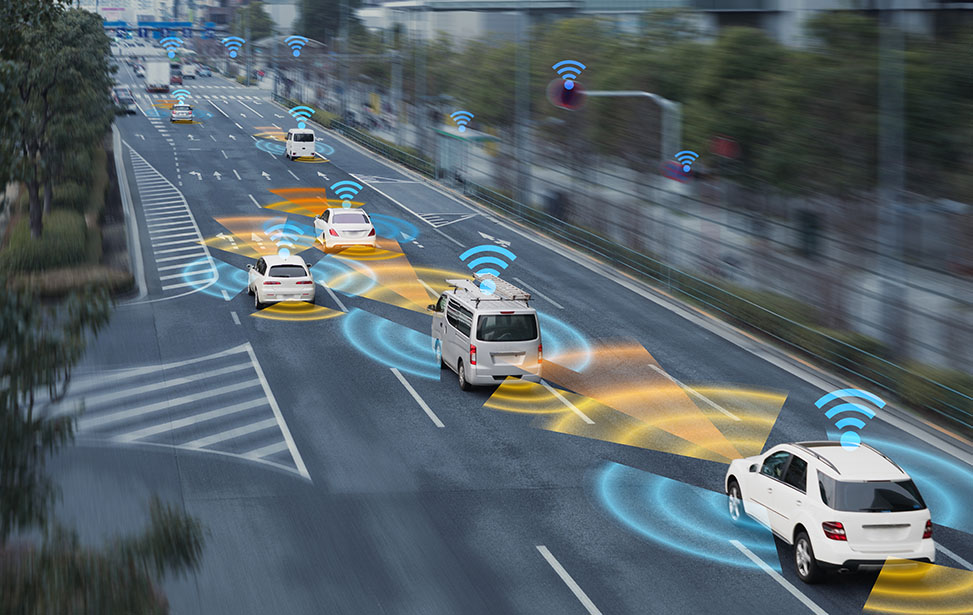
An autonomous vehicle, also known as a self-driving vehicle, is a vehicle that is capable of sensing its environment and moving safely with little or no human control. It is one of the major factors of Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS), which represents the integration of information and communication technologies (ICTs). The main goal of ITS is to achieve a reduction in traffic and pedestrian fatalities, and enhance transport infrastructure systems, through the realization of autonomous driving. Besides ITS, autonomous vehicles also play an important role in future industrial applications such as automated fruit/flower harvesting, automated forklifts, automatic guided vehicle (AGV), etc.
Advanced 8K Panoramic Capabilities
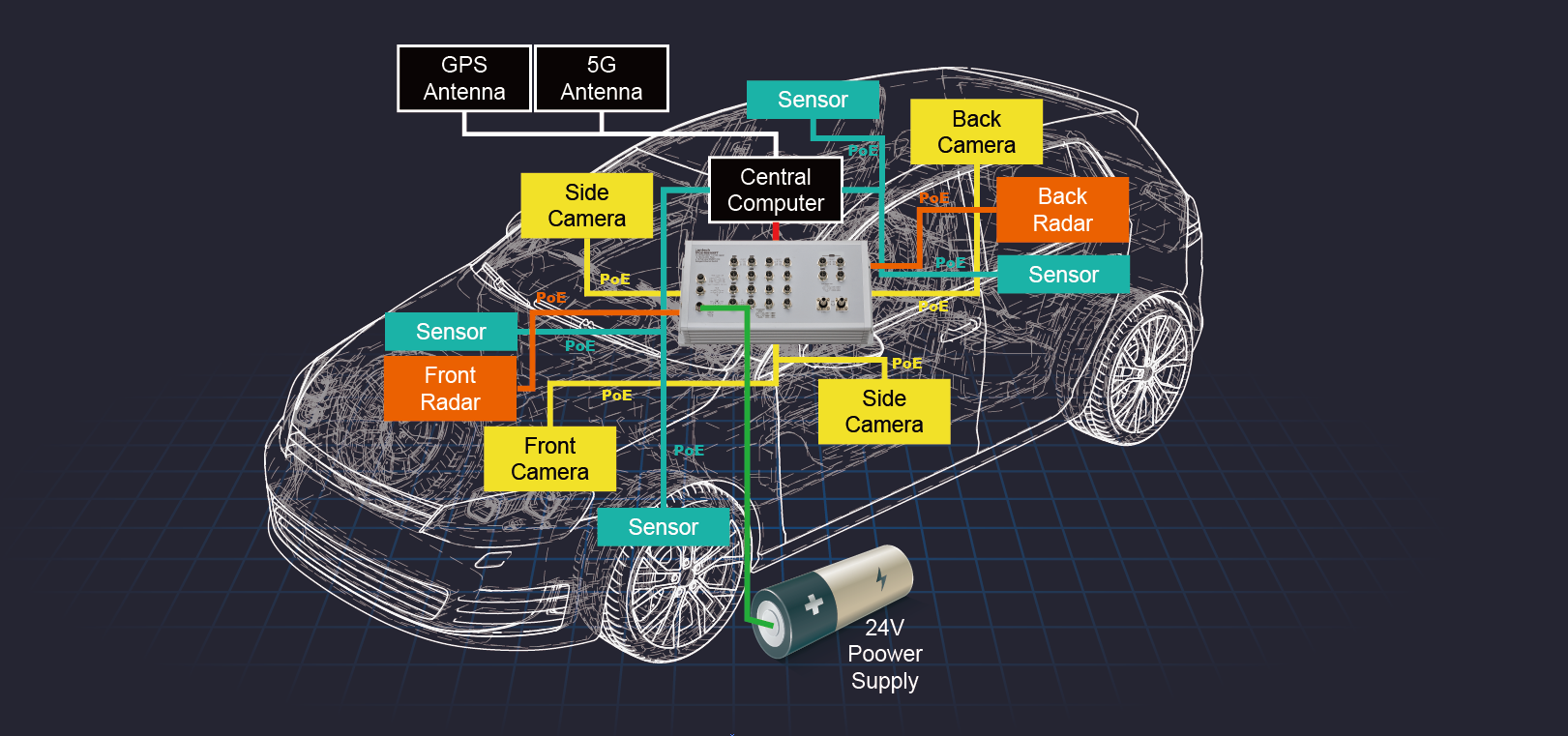
To perceive their surroundings and replicate human driving, autonomous vehicles integrate a variety of components to its sensor and vision systems, that can scale to millions of vehicles and work in diverse lighting and weather conditions. High-quality, ruggedized and precision imaging solutions which include 3D object resolution, static and dynamic object screening, and 360-degree horizontal coverage are adopted. The result of Installing 8K panoramic cameras is vast amounts of real time data being transmitted which in turn requires a large bandwidth capacity.
Real-time 3D Mapping Capabilities
Besides high quality vision solutions, powerful sensor systems that include sonar, radar, GPS, odometry and LiDAR, are also necessary. To provide adaptive cruise control, collision avoidance, and blind-spot detection, a 3D map is generated from the sensor data collected. For example, LiDAR can capture shapes of the environment around the vehicle by scanning its surroundings with a beam of light. Static objects as well as moving ones are tracked in real-time. An automated fruit harvester or an automated forklift may not need 8K high resolution vision quality, however, these autonomous vehicles still integrate optic sensors (cameras), speed or laser sensors, and software to build a 3D map of its operating environment and to navigate the operation. Thus, the massive data transmission requirements are still commonly seen in those applications.





 Lantech is dedicated to providing the best quality and service to our customers. We proudly provide 5 years warranty to our industrial products.
Lantech is dedicated to providing the best quality and service to our customers. We proudly provide 5 years warranty to our industrial products. 
